Analyzing Crime Rates in Canada and the United States: A Complete Comparison
Decoding Crime Statistics: Canada vs. United States
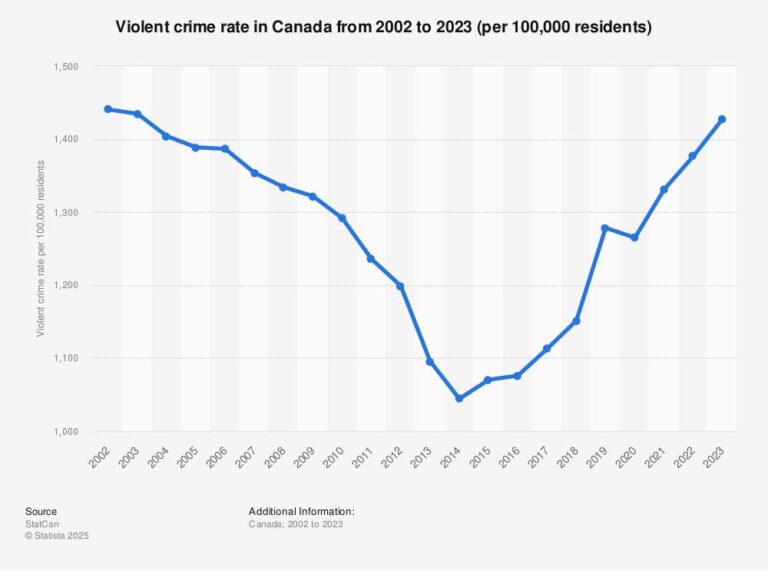
Public safety remains a paramount issue across North America, often prompting comparisons between crime levels in Canada and the United States. Contrary to popular belief,Canada typically reports lower violent crime rates than the U.S. This discrepancy arises from differences in crime definitions, reporting methodologies, and demographic factors such as population density. For instance, while the U.S. experiences notably higher homicide rates,property crime figures between the two countries are relatively similar.
Several critical elements contribute to these variations, including:
- Law enforcement approaches: Canada prioritizes community-oriented policing more extensively.
- Economic disparities: Variations in poverty levels and income distribution influence crime prevalence.
- Firearm legislation: Canada’s stringent gun control laws correlate with fewer gun-related offenses.
| Crime Category | Canada (per 100,000 people) | United States (per 100,000 people) |
|---|---|---|
| Homicide | 1.8 | 5.0 |
| Violent Crime | 1,200 | 3,000 |
| Property Crime | 5,000 | 5,500 |
Key Drivers Behind Crime Patterns in Canada and the U.S.
Crime dynamics in both countries are shaped by a complex interplay of social, economic, and legislative influences. Socioeconomic challenges such as unemployment and limited educational opportunities frequently enough correlate with higher crime rates. The U.S.features larger urban centers where violent crime tends to be concentrated, whereas Canada’s urbanization is more evenly distributed. Additionally, Canada’s comprehensive social safety nets and worldwide healthcare system help mitigate some underlying causes of criminal behaviour, including poverty and mental health issues.
Differences in firearm policies and policing philosophies further distinguish crime trends. The U.S.’s relatively lax gun ownership regulations are linked to increased firearm violence, while Canada’s tighter controls contribute to lower gun-related crime. Cultural attitudes toward law enforcement and community involvement also affect crime reporting and prevention efforts. The table below highlights some contrasting factors:
| Factor | Canada | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Gun Ownership Rate | Approximately 34 firearms per 100 residents | Approximately 120 firearms per 100 residents |
| Recent Unemployment Rate | 6.5% | 5.7% |
| Urban Population Percentage | 81% | 83% |
| Healthcare System | Universal public coverage | Mixed private and public |
- Community engagement programs are generally more prevalent in Canadian cities, aiding crime deterrence.
- The U.S. maintains a higher incarceration rate, reflecting divergent criminal justice policies.
- Variations in public trust toward police affect the accuracy and completeness of crime data.
Socioeconomic Influences on Crime Rates
Economic inequality remains a significant contributor to crime in both nations. Regions grappling with elevated unemployment, insufficient educational resources, and limited social services often see increased criminal activity. Poverty creates environments where lawful income opportunities are scarce, pushing some individuals toward illicit means. These socioeconomic challenges are unevenly distributed, resulting in notable regional crime disparities within each country.
Crucial socioeconomic factors linked to crime include:
- Income disparity: Greater wealth gaps are strongly associated with higher rates of both violent and property crimes.
- Educational attainment: Lower levels of education restrict job prospects, potentially increasing crime involvement.
- Availability of community support: Neighborhoods lacking social infrastructure tend to experience elevated crime.
| Indicator | Canada | United States |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 6.5 | 5.8 |
| Poverty Rate (%) | 11.0 | 12.3 |
| High School Graduation Rate (%) | 89 | 88 |
| Social Expenditure as % of GDP | 20.7 | 15.3 |
Strategies for Effective Crime Reduction
Addressing crime requires a multifaceted approach centered on community involvement and trust-building between law enforcement and citizens. Prioritizing programs that engage youth, provide mental health resources, and emphasize rehabilitation over punishment can significantly reduce criminal behavior. Comprehensive prevention efforts that integrate social services tackle root causes such as poverty, addiction, and educational deficits, thereby limiting crime opportunities.
Implementing data-driven policies enables more efficient resource allocation and better evaluation of crime reduction initiatives. Recommended strategies include:
- Strengthening inter-agency cooperation: Facilitating information exchange across jurisdictions for proactive interventions.
- Leveraging technology: Employing predictive analytics and community monitoring while safeguarding privacy rights.
- Expanding community policing: Increasing officer presence and engagement to foster neighborhood resilience.
- Reforming sentencing: Emphasizing alternative sentencing and restorative justice for non-violent offenders.
| Policy Initiative | Anticipated Outcome |
|---|---|
| Youth Outreach Programs | Reduction in juvenile delinquency |
| Mental Health Interventions | Decrease in recidivism |
| Community Policing Efforts | Enhanced public confidence |
| Data-Informed Resource Deployment | Improved law enforcement effectiveness |
Looking Ahead: Enhancing Public Safety Through Informed Policy
While Canada and the United States each face unique challenges in crime prevention, current evidence indicates that Canada maintains lower overall crime rates. A nuanced understanding of the factors influencing these statistics is vital for shaping effective public safety policies. As both countries continue to evolve socially and economically, ongoing research and adaptive strategies will be essential to monitor crime trends and implement successful reduction measures. For continuous updates and in-depth analysis, follow trusted news sources and official crime reports.