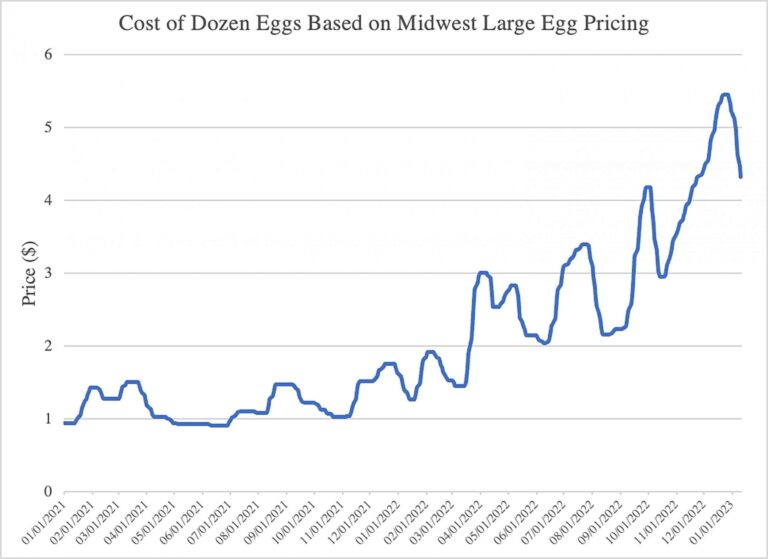
Egg prices have surged to unprecedented levels across the country, and experts warn that the upward trend shows no signs of slowing. Factors including supply chain disruptions, rising feed costs, and the lasting impact of avian flu outbreaks have combined to create a perfect storm for egg producers and consumers alike. As families grapple with higher grocery bills and restaurants face increased operating costs, the implications of this price hike are rippling through the economy.The New York Times examines the key drivers behind the escalating egg prices and what consumers can expect in the coming months.
Egg Supply Chains Strained by Rising Costs and Production Challenges
The egg industry is grappling with a complex web of supply chain disruptions as soaring feed costs, labor shortages, and rising transportation expenses squeeze producers nationwide.Farmers are facing steep inflation on essential inputs like corn and soybeans, which constitute the main components of poultry feed. This surge has pushed operational expenses well beyond previous years, forcing some smaller farms to curtail flock sizes or delay expansions amid uncertain market conditions. Additionally, persistent worker scarcity has led to slower processing times, further tightening supply.
Retailers and wholesalers are responding by adjusting their prices to reflect these mounting pressures,with egg cartons becoming noticeably more expensive on store shelves. The situation is compounded by logistical bottlenecks that delay shipments,and also ongoing biosecurity measures that limit production capacity in some regions due to avian flu outbreaks. The table below highlights key factors currently shaping egg prices:
| Factor | Impact on Supply | Price Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Cost Increase | Reduced profit margins | +15% rise |
| Labor Shortages | Slower production and processing | +8% rise |
| Transport Delays | Increased delivery times | +5% rise |
| Avian Flu Restrictions | Flock reduction in key states | +10% rise |
- Forecasts suggest prices will remain elevated through the next quarter.
- Consumers should prepare for continued volatility in egg availability.
- Industry experts recommend monitoring market trends for potential shifts.
Consumer Impact and What Shoppers Can Expect in the Coming Months
As egg prices continue their upward trajectory, shoppers should brace for a pronounced impact at the grocery store. Consumers may find themselves paying 20% to 30% more per dozen in the near future, driven by a perfect storm of supply chain disruptions, avian flu outbreaks, and increased feed costs. This surge will likely affect not only whole eggs but also egg-based products,including baked goods and processed foods,which commonly use eggs as a key ingredient. Budget-conscious shoppers might need to rethink their purchases, opting for choice protein sources or adjusting meal plans to mitigate rising costs.
Retailers are already strategizing to limit sticker shock, with some introducing smaller pack sizes or promoting egg substitutes. Here’s what consumers can expect:
- More promotions on alternative protein items such as tofu or plant-based egg replacements.
- Increased visibility around egg prices,with stores highlighting reasons for adjustments.
- Potential rationing in extreme cases where supply becomes critically low.
| Product | Current Price (per dozen) | Projected Price (next 3 months) |
|---|---|---|
| Large Grade A Eggs | $3.50 | $4.50 – $4.75 |
| Egg Whites (carton) | $2.80 | $3.50 – $3.90 |
| Liquid Egg Substitute | $4.00 | $5.00 – $5.50 |
Industry Responses and Measures to Stabilize Egg Prices
In response to the soaring egg prices, industry leaders and agricultural stakeholders have mobilized to implement strategic measures aimed at market stabilization. Large-scale producers are ramping up production capacity by investing in advanced poultry farming technologies, while smaller farms are collaborating to optimize supply chains. Retailers are also stepping in, employing pricing controls and promotional discounts to ease the impact on consumers. Additionally,there is a growing emphasis on supply chain transparency to better forecast demand and minimize disruptions caused by health regulations and feed shortages.
Government agencies have introduced several initiatives designed to support both producers and consumers during this volatile period, including:
- Subsidies and grants for feed procurement to reduce production costs
- Temporary import tariff adjustments to increase egg availability
- Enhanced monitoring of market practices to prevent price gouging
- Public awareness campaigns promoting alternative protein sources
| Measure | Responsible Party | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Investment in automation | Producers | Increased production efficiency |
| Pricing guidelines enforcement | Retailers & Regulators | Consumer price stabilization |
| Feed subsidy programs | Government | Lowered operational costs |
| Import adjustments | Trade Authorities | Boosted egg supply |
Strategies for Consumers to Manage Budget Amid Price Volatility
Faced with fluctuating egg prices, consumers can adopt several practical measures to safeguard their budgets without compromising nutritional value. Shopping smart by purchasing eggs during promotional periods or in bulk can substantially reduce the overall cost. Additionally, exploring alternative protein sources such as beans, lentils, or tofu offers nutritional variety while mitigating the impact of rising egg prices. Incorporating flexible meal planning, where recipes can be adjusted based on current market trends, empowers families to remain resilient amid price swings.
Tools for tracking expenses and price changes also play a crucial role.Leveraging apps that monitor grocery price fluctuations can help consumers identify the best times and places to buy eggs and other essentials. Below is a swift guide for budget-pleasant protein options relative to typical egg costs:
| Protein Source | Average Cost per Serving | Protein Content (grams) |
|---|---|---|
| Egg | $0.25 | 6 |
| Dried Beans | $0.15 | 7 |
| Tofu | $0.40 | 8 |
| Lentils | $0.18 | 9 |
- Plan meals ahead: Adjust recipes to incorporate more budget-friendly proteins.
- Buy in bulk: Purchase eggs or alternatives during sales and freeze if possible.
- Opt for local markets: Sometimes small vendors offer better prices than supermarkets.
- Utilize price-tracking apps: Monitor egg prices and receive alerts on discounts.
To Conclude
As egg prices continue to climb and show little sign of easing, consumers and retailers alike face mounting challenges in navigating the evolving market. Factors such as supply chain disruptions, feed costs, and regulatory pressures all contribute to the upward trend, suggesting that the affordability of this staple food may remain a concern for months to come. Monitoring these developments will be essential for understanding the broader impacts on household budgets and the food industry at large.