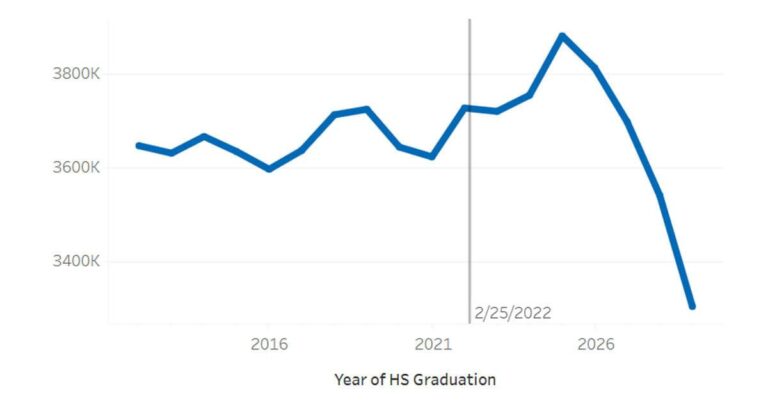
As colleges across the nation grapple with financial instability, shifting enrollment patterns, and mounting operational challenges, a surprising trend is emerging: a record number of students are preparing to enroll in higher education institutions this fall. Despite the crises disrupting the traditional landscape of American colleges, the upcoming academic year is poised to see an unprecedented influx of students seeking degrees and career advancement. This paradoxical development raises critical questions about the evolving role of colleges and their capacity to adapt amid uncertainty, as detailed in a recent report by The New York Times.
Rising Enrollment Despite Financial and Institutional Challenges
Despite ongoing financial strains and a landscape marked by institutional restructuring, colleges nationwide are witnessing an unexpected surge in student enrollment.This phenomenon stands in stark contrast to the broader narratives of crisis within higher education, reflecting a resilient demand for postsecondary education. Factors fueling this trend include the increasing recognition of the value of higher education for career advancement and demographic shifts leading to larger cohorts of college-age individuals.
Institutions are adapting to these pressures by expanding access and diversifying program offerings,even as they grapple with budgetary constraints. Key elements contributing to enrollment growth are:
- Enhanced online learning options that appeal to non-traditional and remote students
- Targeted recruitment efforts aimed at underrepresented communities
- Flexible financial aid packages designed to offset rising tuition costs
| Institution Type | Enrollment Change (%) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Public Universities | +4.3% | Expanded online degree options |
| Community Colleges | +5.8% | Strengthened workforce training |
| Private Colleges | +2.1% | Increased financial aid offerings |
Understanding the Drivers Behind Increased College Applications
Recent data reveals a multifaceted surge in college applications, driven by a confluence of economic, social, and institutional factors. The lingering effects of the global pandemic have reshaped perceptions of higher education, prompting many students to seek stability in academic environments despite widespread financial uncertainties. Additionally, the shifting job market—with a growing emphasis on specialized skills—has made a college degree increasingly desirable as a buffer against economic volatility.
Key contributors to this upward trend include:
- Increased outreach and digital engagement by colleges targeting diverse student demographics.
- Expanded financial aid programs easing access for underrepresented groups.
- Heightened emphasis on mental health resources, positioning colleges as supportive communities.
| Factor | Impact on Applications | Notable Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Uncertainty | Increased interest in degree programs | +15% Applications in 2023 |
| Digital Recruitment | Broader reach, especially international | +20% Online Inquiries |
| Mental Health Resources | Greater student attraction | 45% More Positive Feedback |
Strategies Colleges Are Implementing to Accommodate Growing Student Bodies
Colleges across the country are rapidly adjusting their infrastructures and academic offerings to manage an unprecedented influx of students. Many institutions are expanding on-campus housing by converting existing spaces and investing in new dormitories. Additionally, campuses are leveraging partnerships with local housing providers to ease accommodation shortages. To further alleviate crowding, schools are enhancing virtual learning platforms, allowing a significant number of students to participate in classes remotely without sacrificing educational quality.
Academic departments are also adapting by increasing course sections, hiring adjunct faculty, and optimizing class schedules to accommodate larger cohorts. Guidance offices are scaling up staffing to address heightened demand for student services, including mental health support. Key strategies include:
- Modular classroom constructions to quickly increase instructional space
- Hybrid models blending in-person and online learning
- Extended academic calendars offering year-round sessions
- Enhanced advising tools using AI-powered platforms for personalized student guidance
| Strategy | Impact | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| New Dormitory Construction | +1,200 Beds | 2024-2026 |
| Hybrid Course Expansion | +35% Capacity | Immediate |
| AI Advising Platforms | Improved Student Retention | 2024 Rollout |
| Modular Classrooms | +15 Classrooms | 2025 |
Policy Recommendations to Support Higher Education Amidst Crises
To effectively sustain the surge in college enrollments during turbulent times, policymakers must prioritize increased funding for public institutions, ensuring that they can expand capacity and maintain educational quality.Additionally, enhancing financial aid programs with flexible disbursements tailored to students facing unexpected economic hardships will remove barriers to access for the most vulnerable populations. Expanding mental health services and comprehensive support systems on campuses is equally critical, as students grapple with unprecedented stressors that impact academic performance and retention.
Strategic investments should also focus on innovative learning models that blend online and in-person instruction, providing resilience against future disruptions. Below is a concise comparison of recommended policy actions and their potential impacts:
| Policy Action | Intended Impact |
|---|---|
| Increase Public Funding | Expand enrollment capacity and resources |
| Flexible Financial Aid | Improve access and reduce dropout rates |
| Mental Health Services | Boost student well-being and academic success |
| Hybrid Learning Models | Enhance educational continuity and flexibility |
Key Takeaways
As colleges navigate unprecedented challenges—from financial strain to shifting demographics—the surge in student enrollment signals both possibility and complexity ahead. Institutions must balance expanding access with ensuring quality education and support services, even as they confront broader societal and economic pressures. How these dynamics unfold will shape the future of higher education in profound ways, making it a critical area to watch in the months and years to come.