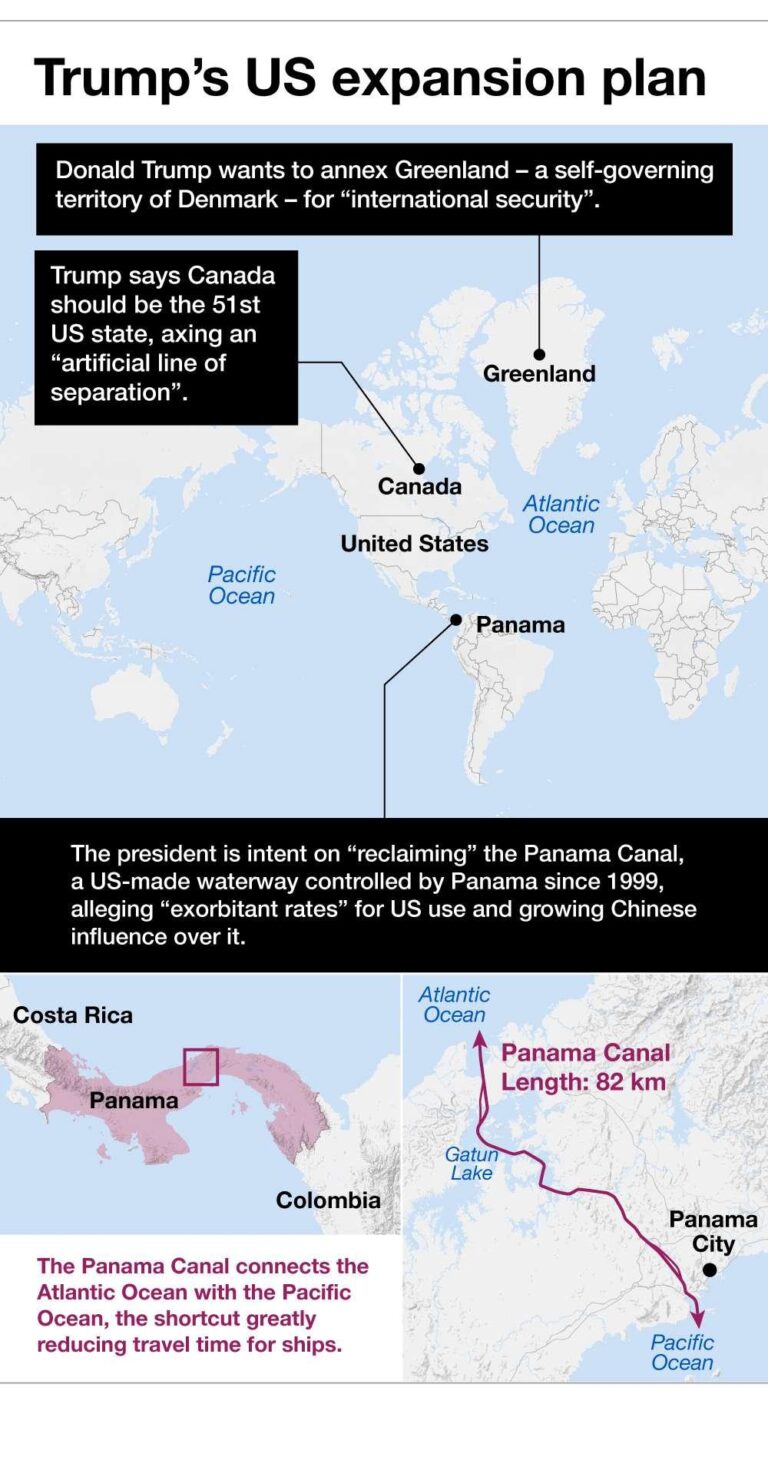
In a surprising twist in U.S.foreign policy, former President Donald Trump’s interest in acquiring Greenland has emerged as a calculated effort rooted more in strategic persuasion than military force. According to a recent report by The New York Times,Trump’s approach to securing the Arctic territory was driven by diplomatic overtures and economic incentives rather than outright invasion. This revelation sheds new light on the complexities behind the controversial Greenland initiative, highlighting a blend of geopolitical ambition and unconventional negotiation tactics.
Inside Trump’s Vision for Greenland Acquisition Efforts
Behind the scenes of the controversial acquisition proposal was a strategy grounded more in negotiation and allure than in forceful tactics. Trump’s approach involved leveraging economic incentives and diplomatic charm, aiming to present the idea as a mutually beneficial chance rather than a opposed takeover. Key appeals focused on Greenland’s vast natural resources and strategic geopolitical position, framed as an investment promising growth and security for both parties.
Central elements of the plan included:
- Economic Partnerships: Proposals for infrastructure development and trade expansions.
- Climate Cooperation: Joint efforts in Arctic research and environmental stewardship.
- Security Alliances: Strengthening defense ties without direct imposition.
| Aspect | Trump’s Proposal | Greenlandic Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Incentive | $ Greenland investment fund | Skepticism about sovereignty loss |
| Security | Enhanced military cooperation | Concerns over foreign military presence |
| Environmental | Arctic research funding | Willingness to collaborate cautiously |
The Role of Strategic Persuasion in U.S. Foreign Policy Moves
In a surprising twist to U.S. foreign policy dynamics, strategic persuasion emerged as the key tool in the Trump administration’s effort to secure Greenland. Rather than deploying military threats or overt coercion, the plan centered around diplomacy laced with calculated pressure, aiming to convince Danish and Greenlandic officials that an American purchase was in their best interest. This nuanced approach underscored a shift toward leveraging economic incentives and political dialog, reflecting a broader trend where influence is increasingly exercised through negotiation rather than confrontation.
Key elements of this persuasion strategy included:
- Economic Appeals: Highlighting potential U.S. investments to boost Greenland’s infrastructure and economy.
- Geopolitical Framing: Positioning the acquisition as vital for regional security in the face of expanding Arctic interests by China and Russia.
- Engagement with Local Leaders: Building rapport and trust with grassroots Greenlandic authorities to soften resistance.
| Persuasion Tactic | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Promises | Economic leverage | Mixed reception |
| Security Emphasis | Strategic urgency | Heightened awareness |
| Diplomatic Outreach | Trust building | Temporary goodwill |
This approach demonstrates how subtlety and persuasion often serve as primary instruments in complex international maneuvers, especially when direct methods risk diplomatic fallout. The Greenland episode serves as a case study in how the U.S. endeavors to balance ambition with tact, illustrating a sophisticated form of strategic influence that transcends customary military avenues.
Analyzing Diplomatic Channels Used to Engage Greenland Authorities
Efforts to diplomatically engage with Greenlandic authorities were marked by a calculated and multifaceted approach. U.S. representatives prioritized personal meetings and informal conversations, aiming to build rapport and trust rather than exert immediate pressure. These interactions frequently enough took place on neutral ground, including diplomatic receptions and cultural events, fostering an environment conducive to open dialogue. Emphasis was placed on respecting Greenland’s autonomy while simultaneously exploring areas of mutual interest, such as economic development, environmental cooperation, and security partnerships.
Official communications supplemented these face-to-face engagements with a series of methodical exchanges.Below is an outline of the primary channels utilized:
- Bilateral Talks: Regular consultations between Greenlandic ministers and U.S. officials.
- Task Forces: Joint groups established to study potential investment and infrastructure projects.
- Cultural Exchanges: Programs aimed at strengthening people-to-people ties and understanding.
- Strategic Proposals: White papers and feasibility studies shared to highlight mutual benefits.
| Diplomatic Channel | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Bilateral Talks | Policy alignment and trust-building | Quarterly |
| Task Forces | Feasibility assessments | As needed |
| Cultural Exchanges | Enhancing mutual understanding | Annually |
| Strategic Proposals | Highlighting shared interests | Occasional formal briefs |
Policy Recommendations for Enhancing U.S.-Greenland Negotiations
To forge a more resilient and mutually beneficial relationship, U.S. policymakers must prioritize dialogue rooted in respect for Greenland’s sovereignty and cultural identity. Rather than leveraging economic pressure or military influence, engagement strategies should focus on partnership and shared interests, especially in areas like climate monitoring, lasting resource development, and Arctic security. Emphasizing clarity and including Greenlandic leaders in all stages of negotiation will help dispel suspicions of coercion, fostering a climate of trust essential for long-term collaboration.
- Prioritize environmental cooperation: Collaborate on scientific research addressing Arctic climate change.
- Support economic diversification: Invest in Greenland’s renewable energy and tourism sectors.
- Enhance cultural diplomacy: Promote educational and cultural exchanges.
- Establish multilateral frameworks: Include other Arctic nations to ensure balanced negotiations.
Analyzing recent negotiation outcomes reveals key areas that require recalibration. The table below outlines potential approaches alongside associated benefits and challenges, offering a roadmap to recalibrate U.S. strategy for more effective dialogue and sustainable agreements.
| Approach | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Scientific Ventures | Builds trust; Advances climate goals | Funding complexities; Coordination logistics |
| Economic Incentives | Boosts local economy; Encourages partnerships | Risk of dependency; Economic disparity concerns |
| Multilateral Dialogue | Reduces unilateral tension; Inclusive strategy | Slower decision-making; Diverse interests management |
Final Thoughts
As the saga of Donald Trump’s Greenland gambit continues to unfold, it offers a revealing glimpse into the unconventional approaches and strategic calculations that defined his presidency. Rather than resorting to military force, the administration’s emphasis on persuasion underscores a nuanced dimension of international negotiation often overshadowed by political rhetoric. While the plan ultimately stalled,the episode remains a compelling case study in diplomacy,ambition,and the complexities of U.S. foreign policy in the Arctic region.