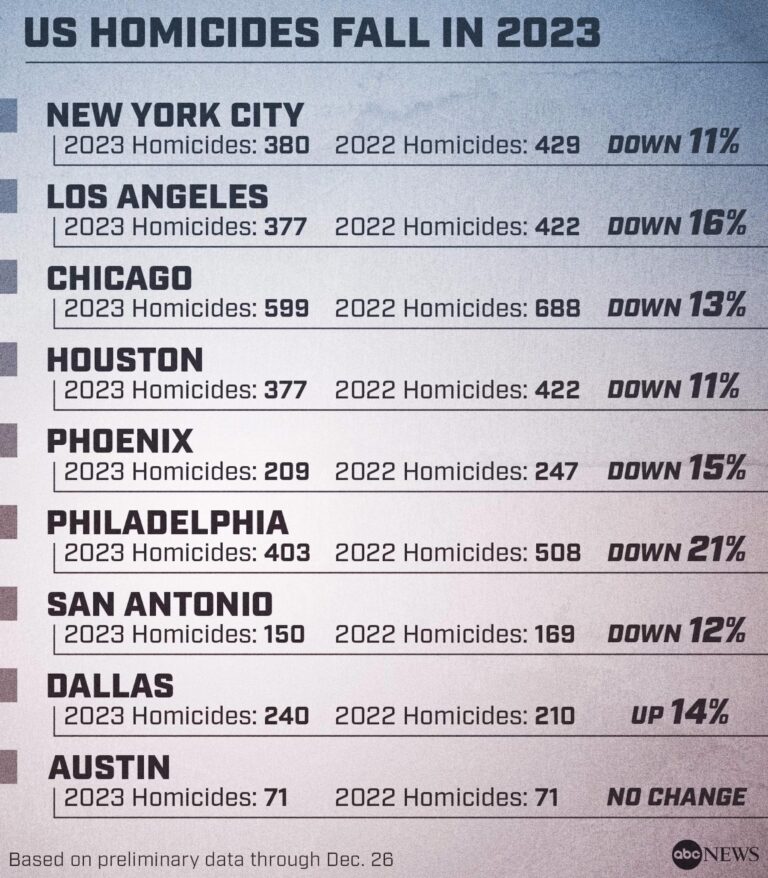
As 2023 draws to a close, the Council on Criminal Justice releases its latest comprehensive report on crime trends across U.S.cities, offering critical insights into the evolving landscape of public safety. This year-end update highlights notable shifts in crime rates, identifies emerging patterns, and examines the impact of policy changes and community initiatives nationwide. The findings provide policymakers, law enforcement, and the public with valuable data to better understand the challenges facing urban centers and to inform strategies aimed at reducing crime in the year ahead.
Crime Rates Shift Across Major U.S. Metropolitan Areas
The landscape of crime across major U.S. metropolitan areas saw notable fluctuations in 2023, with several cities reporting significant shifts in both violent and property offenses. While some urban centers made strides in reducing homicides and aggravated assaults, others contended with rising theft and burglary rates, underscoring the complexity and localized nature of crime dynamics. Key factors influencing these changes included shifts in policing strategies, economic conditions, and community engagement initiatives.
Highlighted trends from recent data include:
- Decreases in violent crime in cities like Seattle and Denver, attributed to increased funding for community policing and social services.
- Rising property crime in metropolitan areas such as Miami and Atlanta, linked to economic volatility and heightened consumer demand.
- Mixed outcomes in large cities like Chicago and Los Angeles, where gains in some crime categories were offset by challenges in others.
| City | % Change in Violent Crime | % Change in Property Crime |
|---|---|---|
| Seattle | -12% | -5% |
| Miami | +4% | +15% |
| Denver | -10% | -6% |
| Atlanta | +7% | +10% |
| Chicago | +1% | -2% |
Emerging Patterns in Violent and Property Crimes Explored
Recent data from the FBI and local law enforcement reveals shifting dynamics within urban crime landscapes across the United States. While several metropolitan areas report significant declines in certain types of violent offenses, others are grappling with unexpected surges. Notably, aggravated assaults and robberies have shown a polarized trend, decreasing in some cities while rising in others due to localized socioeconomic factors. This patchwork pattern underscores the importance of targeted interventions rather than broad policy applications.
Property crimes also continue to evolve, with auto thefts and residential burglaries emerging as principal concerns in suburban and exurban regions. The proliferation of digital technologies has further elaborate trends, as incidents like vehicle hacking blur customary definitions. The table below highlights a snapshot of these patterns in five major U.S. cities,illustrating notable fluctuations from 2022 to 2023.
| City | Violent Crime % Change | Property Crime % Change |
|---|---|---|
| Chicago | -4.5% | +2.3% |
| Los Angeles | +1.8% | -3.0% |
| Atlanta | +7.4% | +5.6% |
| Seattle | -2.9% | +4.8% |
| Miami | +3.2% | -1.1% |
- Focus areas: Assault and robbery variances influenced by community engagement and policing strategies.
- Property crimes: Increasing vehicle-centric thefts require innovative crime prevention technologies.
Impact of Socioeconomic Factors on Urban Crime Dynamics
Recent analyses reveal that urban crime rates are deeply intertwined with a city’s economic and social fabric. Areas grappling with persistent poverty, lack of education, and employment instability continue to experience higher instances of violent crime and property offenses. These factors create environments where criminal activities can flourish, driven by limited legitimate opportunities and heightened social stressors. Studies indicate that neighborhoods with concentrated disenfranchisement see increased challenges in community policing efforts and public safety initiatives,underscoring the critical role socioeconomic upliftment plays in crime prevention.
Key socioeconomic drivers influencing urban crime patterns include:
- Income inequality – Unequal wealth distribution intensifies social tensions and fosters environments conducive to crime.
- Unemployment rates – Job scarcity correlates strongly with rises in theft, drug-related offenses, and violent acts.
- Educational attainment – Lower average education levels correlate with increased crime vulnerability and recidivism.
- Housing instability – Frequent residential mobility and overcrowded living conditions contribute to community disorganization.
| Socioeconomic Factor | Impact on Crime Type | Example City Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Poverty Rate | Higher violent crime rates | Detroit saw a 7% crime increase in low-income zones |
| Unemployment | Rise in property crimes | Chicago’s property crimes rose 5% with job losses |
| Education Access | Correlated with lower youth violence | Denver’s youth offenses dropped 3% with increased school programs |
Policy Recommendations to Enhance Public Safety and Community Trust
To effectively curb rising crime rates while fostering deeper community engagement,policymakers must prioritize multifaceted approaches that go beyond traditional law enforcement. Investing in neighborhood-based programs-such as youth mentorship, mental health resources, and community policing initiatives-has proven instrumental in reducing violent encounters and building trust between officers and residents. Additionally, data-driven strategies should be leveraged to identify crime hotspots, enabling targeted deployment of both social services and public safety personnel.
Further, obvious dialog and equitable justice practices are crucial in restoring faith in the criminal justice system. Below is a snapshot of key policy recommendations backed by recent urban crime data:
| Policy Focus | Recommended Actions | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Expand neighborhood liaison officers | Enhanced public cooperation |
| Rehabilitation Programs | Increase funding for mental health services | Lower recidivism rates |
| Clarity Initiatives | Regular public reporting and audits | Improved accountability |
| Economic Support | Job training and placement for at-risk groups | Reduced crime driven by economic hardship |
- Prioritize collaboration between community leaders and law enforcement
- Implement restorative justice programs to repair relationships and reduce repeat offenses
- Leverage technology for real-time crime analysis while protecting privacy
The Conclusion
As 2023 comes to a close, the latest data on crime trends in U.S. cities underscores the complex and evolving challenges faced by law enforcement and communities alike.While certain cities have made notable strides in reducing violent offenses, others continue to grapple with persistent spikes in specific crime categories. The Council on Criminal Justice’s year-end update provides a critical lens through which policymakers and the public can assess these patterns, informing targeted strategies for the year ahead. Moving forward, sustained collaboration between local authorities, advocacy groups, and residents will remain essential in addressing the root causes of crime and fostering safer urban environments nationwide.