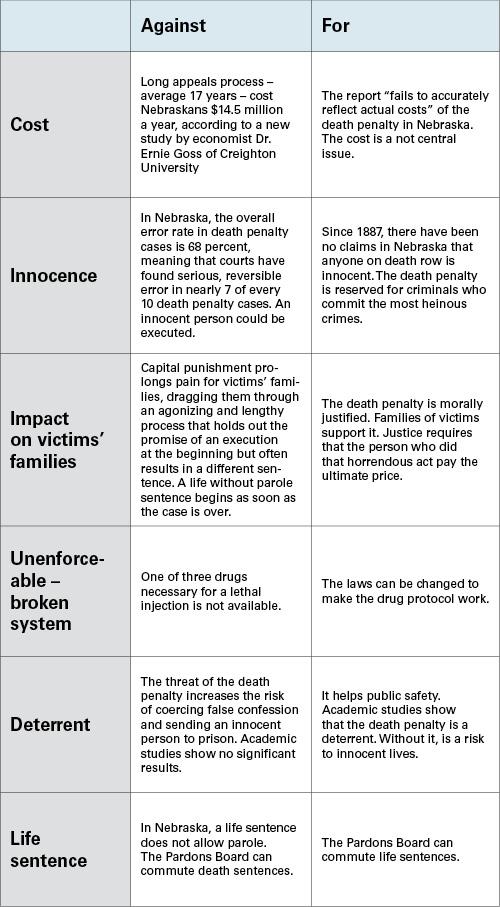
The death penalty remains one of the most contentious issues in criminal justice worldwide, sparking fierce debate over its morality, legality, and efficacy. As societies grapple with how best to address serious crimes such as felonies, questions persist about whether capital punishment serves as a justifiable deterrent or a violation of human rights. This article explores the multifaceted arguments surrounding the death penalty, weighing its pros and cons while examining alternatives like life imprisonment. Drawing on thorough insights from Britannica, it delves into the ongoing debate on capital punishment, prison sentences, and the broader implications for justice systems globally.
Death Penalty Controversy Explored Through Legal and Ethical Lenses
The debate surrounding capital punishment is deeply rooted in complex legal frameworks and profound ethical considerations. Proponents argue that the death penalty serves as a deterrent against heinous crimes, ensures justice for victims, and upholds societal order by permanently removing dangerous felons. They emphasize its role in delivering retribution and closure, especially in cases involving extreme felonies such as murder and terrorism. Conversely, critics highlight the irreversible nature of the punishment alongside its potential for judicial errors, racial and socioeconomic biases, and violation of human rights. Ethicists challenge whether state-sanctioned execution aligns with principles of human dignity and the fundamental right to life.
Key points in the ongoing discussion include:
- Legal safeguards: The rigor of due process and appeals in death penalty cases versus the risk of miscarriages of justice.
- Ethical dilemmas: Balancing punishment, rehabilitation, and the moral ramifications of ending a life.
- Alternative sentences: Life imprisonment without parole as a non-lethal substitute that protects society.
| Aspect | Arguments For | Arguments Against |
|---|---|---|
| Deterrence | Prevents future crimes | No conclusive evidence it deter crimes more effectively |
| Justice | Retribution for victims | Possibility of wrongful execution |
| Ethics | State’s right to punish | Violates human dignity |
Examining the Impact of Capital Punishment on Crime and Justice Systems
Capital punishment remains one of the most divisive topics in criminal justice, with ongoing debates about its effectiveness as a deterrent and its role in ensuring public safety. Supporters argue that the death penalty serves as a crucial tool in curbing heinous crimes, such as murder and terrorism, by imposing the ultimate consequence. They highlight cases where swift capital sentences have arguably prevented repeat offenses and reassured victims’ families, suggesting a strong connection between harsh penalties and crime reduction. Conversely, critics emphasize that numerous studies have failed to establish a clear, causal link between executions and decreased crime rates, questioning whether state-sanctioned death genuinely upholds justice or merely perpetuates a cycle of violence within society.
The impact of capital punishment extends beyond its immediate legal application, influencing prison systems and judicial proceedings.The expensive and prolonged nature of death penalty cases frequently leads to important financial and administrative burdens that some argue could be better invested in rehabilitation and crime prevention programs. Below is a concise comparison highlighting typical outcomes for offenders under different sentencing scenarios:
| Sentence Type | Average Length of Trial | Cost to State | Recidivism Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Death Penalty | 5-10 years | High | 0% |
| Life Imprisonment | 1-3 years | Moderate | Low |
| Long-term Prison | 6 months – 1 year | Low | Moderate |
Issues of fairness, wrongful convictions, and racial disparities also challenge the integrity of capital punishment. Many justice system experts caution that these factors can erode public trust, potentially undermining the legitimacy of law enforcement and judiciary bodies. As debates continue, the balance between punishment, prevention, and human rights remains at the forefront of policy discussions worldwide.
Arguments For and Against Life Sentences Versus Death Penalty Outcomes
When weighing the merits of life sentences versus the death penalty, proponents of life imprisonment often highlight its capacity for redemption and correction. Life sentences allow for the possibility of rehabilitation, enabling offenders to reflect on their actions and potentially contribute positively to society, even from behind bars. Furthermore, this alternative avoids the irreversibility associated with capital punishment, which carries the inherent risk of wrongful executions. Economically, life imprisonment can be more enduring in the long term, considering the costly appeals and legal procedures tied to death penalty cases.
Conversely, advocates for the death penalty argue that it delivers ultimate justice and serves as a deterrent for the most heinous crimes. They claim that capital punishment provides closure for victims’ families and reinforces societal condemnation of egregious felonies.Critics of life sentences also emphasize the financial burden of long-term incarceration and the potential dangers posed by keeping dangerous criminals imprisoned indefinitely. The debate continues, often highlighting moral, legal, and practical dimensions that challenge policymakers worldwide.
| Aspect | Life Sentence | Death Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Reversibility | Possible to rectify wrongful convictions | Irreversible; risk of executing innocents |
| Cost | Lower long-term incarceration costs | Higher due to lengthy trials and appeals |
| Deterrence | Contested impact on crime rates | Viewed by some as stronger deterrent |
| Moral Considerations | Focus on rehabilitation and human rights | Emphasizes retributive justice and finality |
Policy Recommendations for Balancing Felony Punishments and Prison Reform
Striking a balance between appropriate felony punishments and meaningful prison reform requires nuanced policy approaches that prioritize both justice and rehabilitation. Lawmakers are urged to consider alternative sentencing programs for non-violent offenders, such as restorative justice and community service, which reduce incarceration rates while addressing the root causes of criminal behavior. Policies promoting transparency and accountability in sentencing practices can help eliminate disparities that disproportionately affect marginalized communities, ensuring punishment fits the crime rather than systemic biases.Additionally, implementing robust educational and vocational training within correctional facilities can enhance prisoner reintegration, lowering recidivism and fostering public safety.
Strategic investments in prison infrastructure and reform initiatives should be accompanied by clear legislative guidelines that categorize felonies with attention to severity, intent, and potential for rehabilitation. The table below summarizes key recommendations to harmonize felony sentencing with ongoing reform efforts:
| Policy Area | Advice | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sentencing Reform | Expand alternatives for non-violent felonies | Reduced prison overcrowding |
| Rehabilitation Programs | Mandatory education and job training | Lower recidivism rates |
| Transparency Measures | Standardize sentencing guidelines | Fairer, unbiased punishments |
| Prison Conditions | Invest in humane facility upgrades | Improved inmate well-being |
To Wrap It Up
As the debate over the death penalty continues to evoke strong opinions on both sides, its complexities remain undeniable. Balancing justice, deterrence, and human rights presents a persistent challenge for lawmakers and society alike. Whether viewed as a necessary measure for severe crimes or as an outdated, inhumane practice, capital punishment sparks critical conversations about the nature of justice and punishment. As legal systems evolve and public sentiment shifts, the future of the death penalty remains uncertain, ensuring the discussion will persist in the years to come.