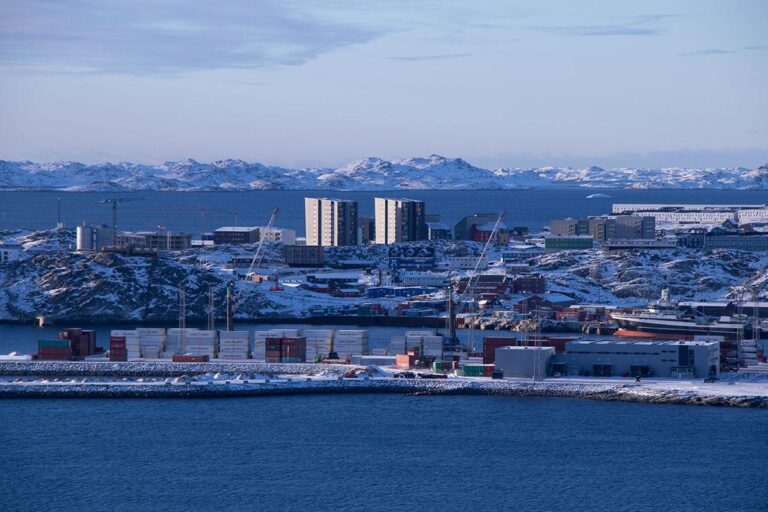
In a remarkable turn of events that captivated global attention, Greenland has firmly rejected recent overtures to purchase the vast Arctic territory, reaffirming its sovereignty with a clear message: “We’re not for sale.” Yet, in an unexpected show of diplomacy, Greenland’s leaders have extended an olive branch, signaling a willingness to engage in dialog on economic and strategic partnerships. This nuanced stance emerges amid heightened geopolitical interest in the region’s natural resources and strategic location. The New York Times explores the intricate dynamics behind Greenland’s response to the controversial proposal,shedding light on the evolving relationship between Greenland and the United States.
Greenland’s Strategic Value Beyond Real Estate
Greenland’s significance extends far beyond its vast tracts of ice and potential real estate transactions. As global interest in the Arctic intensifies, the island occupies a critical vantage point for geopolitical strategy. Its proximity to emerging polar shipping routes offers unprecedented access to new trade pathways that could redefine global commerce. Additionally, Greenland’s rich reserves of rare earth minerals and untapped energy resources underscore its importance in the shifting balance of international power dynamics.
Key factors that elevate Greenland’s influence include:
- Access to Arctic Passageways — These routes could slash travel times between Asia,Europe,and North America.
- Natural Resources — Encompassing rare earth elements vital for technology and energy sectors.
- Scientific Research — Serving as a hub for climate and geological studies that drive global environmental policies.
| Strategic Element | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Shipping Routes | Reduced transit times, lowered costs |
| Mineral Reserves | Critical for tech industry growth |
| Geopolitical Leverage | Increased influence in Arctic policymaking |
Balancing Sovereignty and Economic Opportunity
Greenland’s leadership remains firm: national sovereignty must never be compromised.While the island’s vast natural resources and strategic position have attracted international interest, especially from the U.S., officials emphasize that any engagement must respect Greenland’s autonomy.The priority lies in making informed decisions that bolster Greenland’s future without yielding to external pressures. This has led to a delicate dance where diplomacy and economic pragmatism coexist, allowing Greenland to safeguard its heritage while opening doors to mutually beneficial partnerships.
Economic opportunity is a rising priority, particularly as the Arctic’s changing landscape creates new avenues for investment.Greenland is exploring ventures in:
- Renewable energy projects,including wind and hydroelectric power
- Mineral extraction,with strict environmental oversight
- Tourism,capitalizing on pristine,untouched landscapes
By balancing careful stewardship with strategic collaboration,Greenland aims to create a resilient economy. The following table highlights potential key sectors and their projected impact:
| Sector | Potential Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Sustainable growth, job creation | Infrastructure growth, funding |
| Mineral Resources | Economic diversification, global demand | Environmental concerns, regulatory hurdles |
| Tourism | Cultural exchange, revenue generation | Seasonal variability, infrastructure limits |
Diplomatic Nuances in US-Greenland Relations
In the evolving landscape of US-Greenland relations, the dialogue transcends mere transactional negotiations. Greenland’s government has firmly emphasized its sovereignty and the intrinsic value of its vast natural resources, making clear that any relationship with the United States will be built on mutual respect rather than a simple purchase agreement. This underscores a broader diplomatic stance that Greenland is open to investment and collaboration but not at the expense of its autonomy or cultural heritage.
Key points shaping the diplomatic discourse include:
- Greenland’s assertion of self-governance and strategic importance in the Arctic region.
- The United States’ interest in strengthening security ties and accessing rare earth minerals.
- Opportunities for economic development through sustainable partnerships rather than outright acquisition.
| Diplomatic Element | Greenland’s Outlook | U.S. Position |
|---|---|---|
| Sovereignty | Non-negotiable and prioritized | Respects autonomy but seeks influence |
| Economic Collaboration | Favors joint ventures | Interested in strategic investments |
| Military Presence | Allows with conditions | Seeks Arctic security advantage |
Recommendations for Sustainable Engagement and Investment
To foster meaningful and sustainable partnerships in Greenland, stakeholders must prioritize environmentally responsible investments that respect the island’s delicate Arctic ecosystem.Emphasizing transparency in negotiations ensures that any development project aligns with local community values and long-term ecological preservation. Investors and policymakers alike should commit to ongoing dialogue that balances economic goals with Greenland’s unique cultural heritage and environmental stewardship.
Key strategies for sustainable engagement include:
- Collaborative decision-making: Involving indigenous leaders and local authorities at every stage.
- Impact assessments: Conducting thorough social and environmental studies before proceeding.
- Adaptive governance: Establishing frameworks that can evolve with emerging scientific data and community feedback.
- Long-term investment horizons: Prioritizing projects with durable benefits over short-term gains.
| Investment Focus | Potential Benefit | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Energy independence, job creation | Community training programs |
| Sustainable Tourism | Economic growth, cultural exchange | Eco-kind infrastructure |
| Fisheries Management | Resource conservation, food security | Quotas and monitoring systems |
Concluding Remarks
As the dialogue around Greenland’s strategic value unfolds, the island’s clear message resonates: while it refuses to be treated as a commodity, it remains open to discussions that respect its sovereignty and economic interests. This episode underscores the complexities of international relations in the Arctic region, where resource potential and geopolitical considerations intersect. Moving forward, Greenland’s stance serves as a reminder that negotiations must balance national dignity with pragmatic engagement—a dynamic that will continue to shape the evolving narrative between Greenland, the United States, and the broader global community.