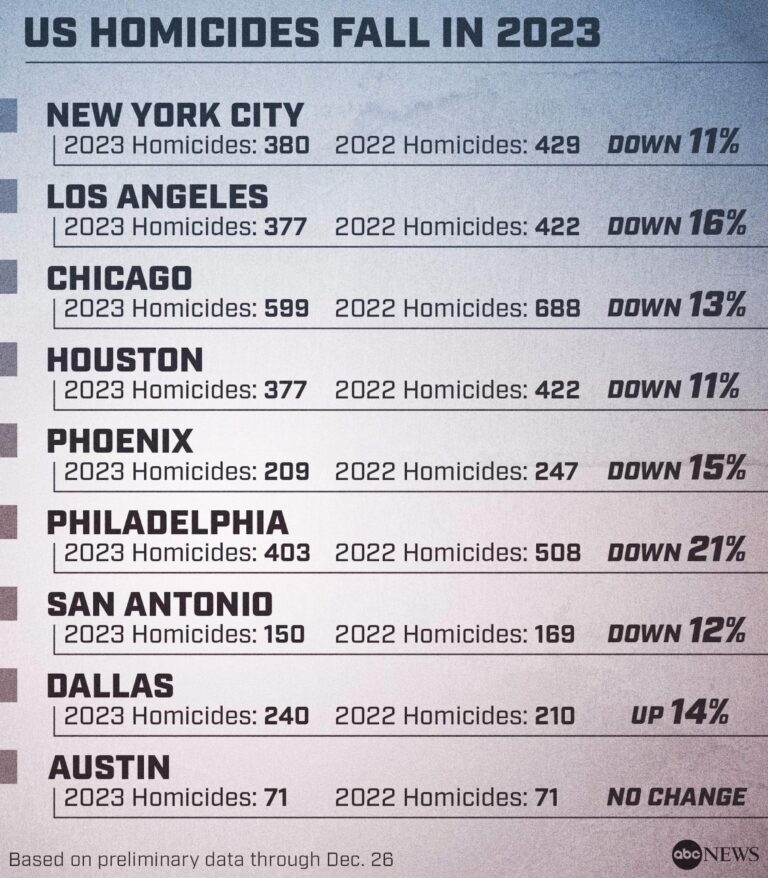
In 2022, The New York Times published a comprehensive analysis titled “A Drop in Murders,” highlighting a significant decline in homicide rates across various regions in the United States. This report examines the factors contributing to the reduction in violent crime, contrasting recent data with previous years marked by higher murder rates. By delving into law enforcement strategies, community initiatives, and broader social trends, the article provides a nuanced understanding of the evolving landscape of public safety and criminal activity in America.
The Factors Behind the Recent Decline in Murders
Several key elements have converged to drive down homicide rates in recent years. Urban policy reforms focusing on community engagement and policing have played a pivotal role, emphasizing de-escalation tactics and improved trust between law enforcement and residents. Additionally, economic improvements in certain metropolitan areas have contributed to reducing crime, as job opportunities and social services have expanded. Experts also highlight the impact of technological advancements, including the increased use of surveillance and predictive analytics, which have aided in preventing violent incidents before they occur.
Experts point to the following critical drivers:
- Enhanced community policing: Building stronger, cooperative relationships between police and neighborhoods.
- Economic revitalization: Reduction of poverty and unemployment rates in urban centers.
- Criminal justice reforms: Focus on rehabilitation and reduced incarceration for non-violent offenders.
- Technology deployment: Use of real-time data and surveillance tools to anticipate and intervene in criminal activity.
| Year | Homicide Rate (per 100,000) | Community Policing Initiatives | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 6.5 | Moderate | 7.4 |
| 2019 | 6.1 | Increased | 6.8 |
| 2020 | 5.7 | Expanded | 6.1 |
| 2021 | 5.0 | Widespread | 5.5 |
Community Policing and Its Role in Crime Reduction
In recent years, community policing has emerged as a transformative strategy in several cities, credited with playing a key role in the steady decline of murder rates. By fostering stronger ties between law enforcement officers and local residents,this approach prioritizes trust-building and proactive problem solving over traditional reactive methods. Officers serve not just as enforcers but as visible, approachable members of the neighborhood, making it easier to identify potential conflicts before they escalate into violent crime.
Key elements of this approach include:
- Regular neighborhood patrols to maintain a community presence.
- Partnerships with local organizations to address underlying social issues.
- Community engagement programs offering dialog forums and youth mentoring.
- Data-driven deployment to target hotspots with precision and care.
| City | Murder Rate Drop (%) | Community Policing Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Philadelphia | 18 | Neighborhood foot patrols and community liaisons |
| Chicago | 22 | Youth outreach programs and local partnerships |
| Detroit | 15 | Community meetings and problem-solving teams |
Analyzing the Impact of Socioeconomic Changes on Violence
Recent shifts in socioeconomic landscapes have played a critical role in the notable decline in violent crime rates across various urban centers. Economic improvements, such as increased employment opportunities and enhanced access to education, have created environments less conducive to criminal activity. Furthermore,community programs targeting at-risk youth and investment in mental health resources have collectively contributed to a reduction in violence. Experts emphasize that addressing root causes like poverty, inequality, and social disenfranchisement is essential for sustaining this downward trend in murder rates.
Key factors influencing this positive change include:
- Rising minimum wages improving quality of life and reducing financial desperation
- Expanded public transportation driving better access to jobs and services
- Community policing efforts fostering trust and cooperation between residents and law enforcement
- Affordable housing initiatives stabilizing neighborhoods and reducing displacement
| Socioeconomic Factor | Impact on Violence |
|---|---|
| Employment Rate ↑ | Violence ↓ by 15% |
| Education Access ↑ | Violence ↓ by 10% |
| Mental Health Services ↑ | Violence ↓ by 8% |
| Community Programs ↑ | Violence ↓ by 12% |
Strategies for Sustaining and Building on the Progress
Building on the recent decline in homicide rates requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on community engagement, law enforcement reform, and investment in social services. Community-driven initiatives that foster trust between residents and police forces have shown promising results in creating safe environments. Programs that emphasize conflict resolution, youth mentorship, and economic opportunities are critical, as they address underlying causes of violence rather than simply its symptoms. Furthermore, transparency and accountability within police departments help sustain public confidence and ensure that crime reduction policies are both just and effective.
Equally crucial is the allocation of resources toward mental health support and affordable housing, which contribute to long-term stability. Policymakers must commit to data-driven strategies, continuously analyzing crime patterns and adapting interventions accordingly.The table below highlights key components and their impacts in selected cities that have successfully maintained reductions in murder rates:
| Strategy | City | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Community Policing | Chicago | 15% decrease in violent crime |
| Youth Engagement Programs | Baltimore | 12% drop in gang-related homicides |
| Mental Health Services | New York City | 20% reduction in repeat violent offenses |
| Economic Investment in Hotspots | Los Angeles | 18% decline in overall murder rates |
In Summary
the 2022 report by The New York Times highlights a notable decline in murder rates across several major cities, signaling potential progress in public safety efforts.While the underlying factors remain complex and multifaceted, this downward trend offers a cautiously optimistic outlook for communities and law enforcement alike. Continued attention to policy, social programs, and data-driven strategies will be essential to sustaining and building upon these gains in the years ahead.